Manufacturing of Machine Tool castings
Material selection
More than 80% of machine tool castings on the market are made of gray cast iron. The many characteristics and advantages of gray cast iron determine, it is one of the most suitable materials for making machine tool castings.
Advantages of grey iron castings:
- Gray cast iron has better casting performance and cutting performance
Compared with cast steel, the melting temperature of gray cast iron is lower, and the smelting equipment and smelting process are relatively simple.
- The fluidity of the gray cast iron melt is good, which makes the castings have goodformability and are not easy to crack.
- The graphite in gray cast iron is in the form of flakes, and this graphite structure makes gray cast iron insensitive to cuts.
- Gray cast iron has good wear resistance.
The graphite in gray cast iron acts as a beneficial lubricant, and the cavities formed after the graphite flakes off from the matrix provide convenient storage for lubricating oil. This feature makes gray cast iron a good wear-resistant material .
- Gray cast iron has good shock absorption properties.
The flake graphite in gray cast iron is equivalent to a cavity, which plays a certain role in splitting the matrix. It can accelerate the attenuation of vibration energy when it encounters vibration, so it has good shock absorption performance.
Castings Processes:
Lost Foam:


- Lost foam does not require the production of permanent molds or special sand boxes, and is suitable for small batch and multi-variety orders.
- Simplify the molding process by eliminating the need for box closing or mold removal, thus avoiding casting defects caused by box closing and mold removal.
- Traditional casting processes do not limit the shape of parts produced by lost foam casting, reducing the workload of mechanical designers and enabling them to design the required casting shape based on the performance of the part. Set the pouring riser of suitable shape at the ideal position without considering factors such as parting and mold taking, thus reducing the internal defects of the produced castings.
- During the pouring process, the white mold will absorb heat, causing the temperature difference of the molten iron entering the mold to be too large. The low-temperature molten iron at the front end will cause insufficient gasification of the white mold, resulting in carbon deposition.
- When using lost foam casting, if the pouring temperature is too low, the white mold will be insufficiently vaporized. The liquefied white mold will contaminate the dry sand, reduce its air permeability, and increase the probability of pores.
Permanent Mold(Wooden Molds/Metal Molds)


- Can be reused, low cost, suitable for large castings and small batch production.
- The mold is made with high precision and the castings produced are of high precision.
- Mold production takes a long time and the initial investment is high.
Methods and importance of heat treatment of machine tool castings:

- Heat the machine tool casting to the appropriate temperature, heat it to the appropriate temperature, adopt different holding times according to the material and workpiece size, and then slowly cool it. The purpose is
- Making the internal structure of the metal reach or approach an equilibrium state, obtaining good process performance and usability, and eliminating internal stress.
Machining of machine tool castings
- Machine tool parts are typically processed through rough machining, followed by secondary heat treatment or aging treatment, finishing, and finally, rail surface grinding.
- Machining equipment used:
Vertical machining centers:

Large gantry machining centers:

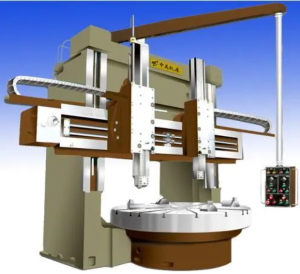
Large vertical lathe:
Large gantry grinder:

Common types of machine tool castings
Base of Vertical Machining Centers:

Gantry machining center castings:


Lathe inclined bed:


